Accurate measurement and monitoring of temperature can be regarded as one of the most critical functions in industrial operations. It not only ensures the final quality of temperature-sensitive products but also prevents financial losses worth millions by minimising equipment downtime. Furthermore, in high-risk industries such as chemical, petrochemical, and nuclear, effective temperature monitoring plays a pivotal role in safeguarding countless human lives.
For example, in June 2025, a pharmaceutical facility in Telangana, India, experienced a tragic incident where the failure to detect the overheating of Microcrystalline Cellulose (MCC) inside a dryer resulted in an explosion that claimed several lives. Although such occurrences are relatively rare today, the case underscores the critical importance of proper temperature monitoring and maintenance, as well as the severe consequences that can arise from lapses in these measures.
A more frequent issue is equipment downtime caused by failures linked to inadequate temperature monitoring, which can cost manufacturers anywhere from $5,000 to $100,000+ per hour, depending on the size of the facility and the industry. Hence, today’s industries require systems that are not only accurate but also intelligent, capable of making minor adjustments to minimise or even prevent downtime. Fortunately, for temperature measurement, the solution already exists in the form of Smart Temperature Transmitters (STTs), and according to Stratview Research, in 2025 alone, a combined demand for ~2 million units of STTs is expected to be generated globally.
Time is money, and STTs save both
Minimising equipment downtime and enhancing operational efficiency by maximising productive hours remain the top priorities for any industrial operation, and STTs directly address these needs in multiple ways. Beyond offering significant advantages over traditional temperature transmitters, such as remote calibration and monitoring, self-diagnosis, and the ability to process inputs from multiple sensors, they are also designed to be easier to install and maintain.
One way STTs help reduce maintenance costs is through their self-diagnosis capability, which includes features such as integrated sensor-break detection and Namur 89 wire-break identification. This minimises the need for frequent manual inspections, thereby lowering overall maintenance expenses. Additionally, STTs such as those from Honeywell’s SmartLine portfolio offer multi-point calibration that claims to save up to two hours per recalibration. Additionally, STTs from top suppliers that come with a modular design further claim to save up to three hours per installation, significantly reducing non-operational hours during setup.
Additionally, STTs integrate seamlessly with Process Knowledge Systems (PKS), further enhancing operational efficiency and simplifying monitoring. Leading STT manufacturers claim that, when connected to the suitable PKS, the efficiency of STTs can be improved by as much as 40%.
Beyond their robustness, STTs are also highly precise. Premium models can deliver accuracy levels of up to ±0.1°C, a capability particularly critical in high-risk or high-precision industries such as pharmaceuticals, semiconductors, oil & gas, and nuclear.
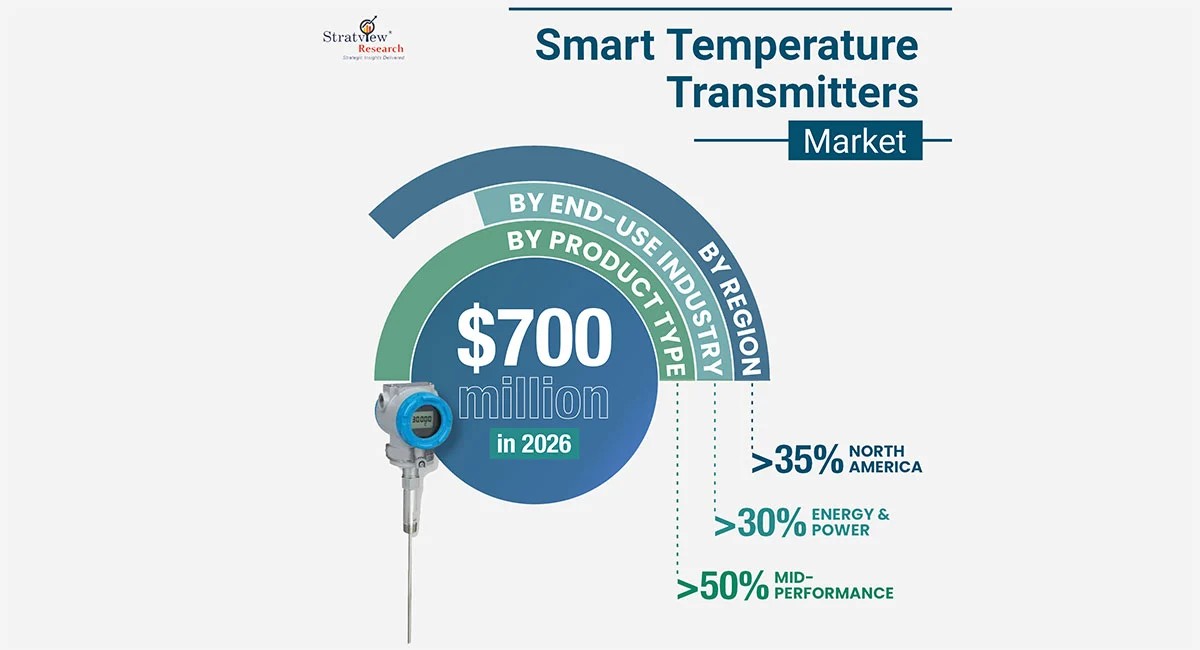
For most other industries, however, standard STTs are more than sufficient. In fact, according to Stratview Research, on a global scale, the mid-tier segment is expected to drive the majority of demand, with nearly 60% of global STT requirements expected to come from this category.
In the premium, or high-performance, segment, the oil & energy industry is anticipated to generate the highest demand. Interestingly, this sector also leads the overall market, with an expected share of approximately 30%.
Predictive maintenance assisting in predicting the market curve
One of the key drivers of STT demand in today’s market is the relentless push by manufacturing units to bring the unplanned downtime close to zero. Since most errors in operations occur at random instances, bringing the downtime close to zero is only possible through continuous monitoring, which, in turn, is possible by adapting Predictive Maintenance (PdM) methods.
According to a 2024 global survey by MaintainX, which covered more than 1,000 OEMs across regions and sectors, approximately 45% identified reducing downtime as their primary objective for adopting predictive maintenance (PdM). However, despite the strong adoption intent, active usage remains limited. The same survey revealed that only 30% of respondents actively implemented predictive maintenance in their operations, thus leaving a huge room for opportunities.
PdM alone can enhance performance by an average of 15-20%. When combined with AI and ML, this improvement can reach up to 30%. In addition, PdM consistently reduces maintenance costs by approximately 20%, irrespective of the industry in which it is applied.
Consequently, manufacturers face diminishing barriers to adopting these benefits, and many are already investing in smarter production systems, incorporating critical elements like Smart Temperature Transmitters (STTs). While granular adoption rates vary, the growing embrace of predictive maintenance, driven by measurable gains in performance and cost efficiency, highlights its undeniable strategic importance.
Driven largely by the growing adoption of predictive maintenance (PdM) practices and the sustained emphasis on worker safety, the global Smart Temperature Transmitters market is projected to reach approximately $700 million by 2026, according to Stratview Research.
Addressing the spike hurdles
While most of the industry acknowledges the importance of transitioning to smart systems such as PdM and STTs, adoption has not been entirely seamless. Two key factors contribute to this. First, despite being cost-effective in the long run, the upfront investment required for implementing STTs or PdM systems poses a challenge. Second, in many regions, factory workforces are not adequately trained in the intricacies of advanced AI- and ML-based operations, resulting in a significant skill gap.
While challenges exist for STTs, like any other technology or equipment, the transformative impact in reducing downtime, enhancing efficiency, and safeguarding operations ensures they will remain a cornerstone of the modern industrial landscape.
Authored by Stratview Research. Also published on - Electronic Specifier.