With the global population set to reach 8.5B by 2030 and a rising aging population, demand for radiology is increasing. Stratview Research projects the digital radiology market to surpass $6.5B by 2028, growing at ~7% CAGR, driven by more imaging studies and outpatient services.
Medical imaging is the keystone of modern health care. It enables about 70% of clinical diagnoses and accounts for 80% to 90% of all hospital data. The World Health Organization (WHO) claims that, globally, more than 3.6 billion diagnostic radiology examinations are performed each year.
Globally, there is a significant shortage of radiologists. An alarming fact from the WHO indicates that two-thirds of the globe does not have access to basic radiology services.
The availability of radiologists doesn’t seem to be matching the growth rate of the population or the demand for imaging. India, for example, the most populous country in the world, has merely 20,000 radiologists to serve a population of over 1.4 billion. This is an alarming ratio of just one radiologist for every 100,000 individuals, far below many developed and developing countries. Europe has 13 radiologists per 100,000 people. In the United Kingdom, the rate is ~9 per 100,000. While countries such as the United Kingdom and the United States have thousands of radiologists to serve their citizens, some countries in the sub-Saharan Africa region do not have a single radiologist.
The shortage of radiologists has far-reaching consequences for health care systems and patients worldwide. The COVID-19 pandemic exacerbated this crisis, claiming countless lives. Radiology played a pivotal role during the pandemic, placing immense strain on already overburdened radiology departments. Radiologists faced unprecedented workloads, compromising work-life balance and overall well-being.
The major challenges facing the radiology industry today include the following:
- lack of radiologists;
- radiation exposure;
- high patient throughput time; and
- cost.
However, radiology is at the threshold of a revolution with the coupling of DR with new-age technologies, especially AI.
Emerging Technologies
To address the growing need for radiology and the lack of radiologists, the demand for digitalization of radiology has increased, and technical advancements such as AI have emerged as game changers. AI improves diagnostic accuracy in DR, reducing processing time, streamlining workflows, and ultimately assisting radiologists in benefiting patient care.
There are several radiology tools that integrate AI to get quick and reliable results, almost better than a human. Gleamer’s BoneView, for example, can help radiologists reduce reading time by ~35% and has ~22% more sensitivity to multifractures, possibly leading to reduced diagnostic errors. Researchers estimate that nearly 800,000 Americans die or are permanently disabled by diagnostic errors each year. Implementing AI for better results will likely save lives. BoneView also claims that it can save ~27% time in patient throughput.
Automatic image stitching is another game changer in DR, breaking the barriers of image size limitations and enhancing diagnostic precision. This technique seamlessly combines multiple images into a single frame for clarity. It is preferred for advanced orthopedic scans where performing long lengths imaging is required. In a research experiment, around 40 pairs of X-ray images of patients with lower limb abnormalities were stitched without manual input using this technique. Compared with previous imaging methods, this improved integration provided more accurate and faster results, covering even small overlaps.
The rise of portable and point-of-care digital radiography solutions is another significant development that expands the scope of the DR industry. Portable and point-of-care DR solutions enable health care professionals to capture high-quality X-ray images directly at the patient's bedside or in various clinical settings, including emergency departments and mobile imaging units.
AI Ahead
The global population is expected to cross 8.5 billion by 2030 and to increase to 9.7 billion by 2050, according to the United Nations. According to the WHO, one in six people in the world will be aged 60 years or older by 2030. With a growing and aging population comes several health conditions requiring radiology. The trend of outpatient services is also growing, leading to more imaging studies and creating more opportunities for the DR industry and professionals associated with it. According to Stratview Research, the global digital radiology market is projected to cross $6.5 billion in 2028, growing at a compound annual growth rate of ~7%.
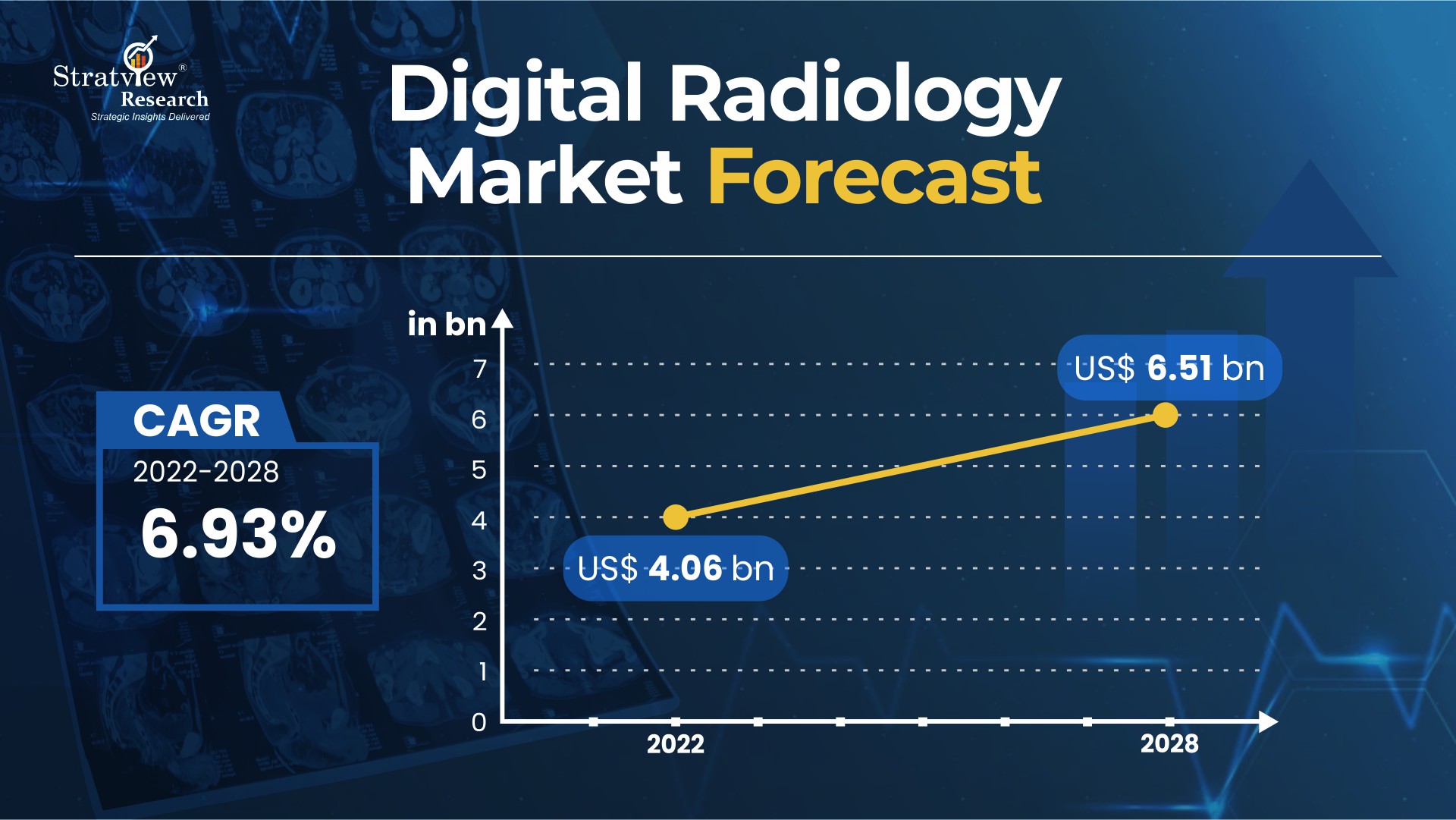
Fig 1 : Digital Radiology Market Forecast
The growing volume of digital data generated from imaging studies is creating a pressing need for effective storage solutions. A number of businesses have started investing in cloud-based solutions.
In 2024, there were notable acquisitions by health care giants of AI businesses, such as the acquisition by GE HealthCare of Intelligent Ultrasound Group PLC, which aims to address inefficiencies and improve patient care quality by providing real-time support via AI-enabled devices.
Royal Philips, a global health care technology leader, collaborated with the cloud solution giant Amazon Web Services, aiming to improve workflow in digital pathology solutions in the cloud to help accelerate decision-making.
Rad AI aims to use Google’s cloud platform and AI tools—including MedLM, a foundation model for the health care industry—in their recent collaboration. This collaboration also aims to save radiologists’ time, improve image quality, and improve the quality of patient care.
DR, coupled with disruptive technologies such as AI, has revolutionized the field of medical imaging, offering significant advantages to both health care providers and patients. As technology continues to evolve, hospitals and diagnostic clinics will increasingly adopt DR and AI, making the potential of these technologies more evident than ever before.
Authored by Stratview Research. Also published on – Radiology Today
